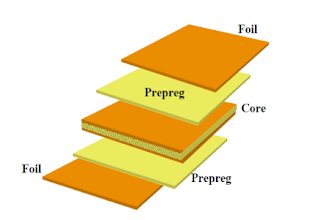
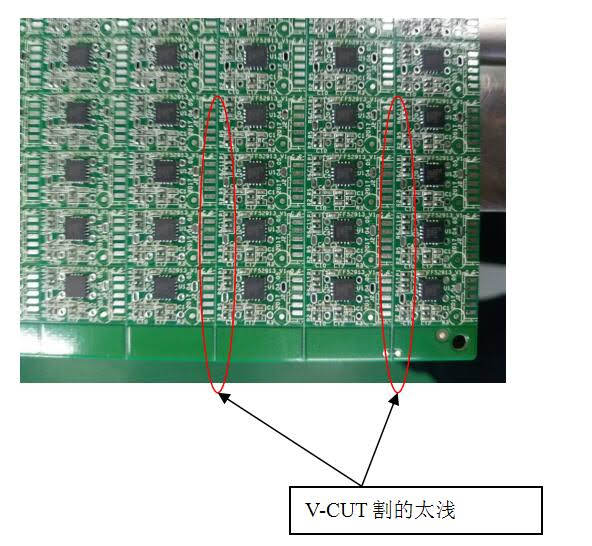
How pcb is manufactured?
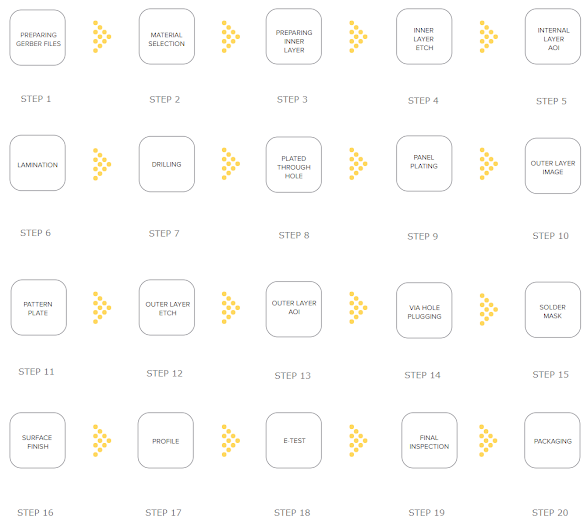
The manufacturing of a Printed Circuit Board (PCB) is a complex process that involves several steps. Here is an overview of how PCBs are typically manufactured: 1. Design and Layout: The PCB manufacturing process begins with the design and layout of the PCB. Designers use PCB design software to create a schematic diagram of the circuit and then lay out the components and traces on the PCB to ensure proper connectivity. 2. Gerber File Generation: Once the design is complete, the designer generates Gerber files. These files contain detailed information about the PCB's layers, component placements, and traces. Gerber files are essential for the fabrication process. 3. Material Selection: The next step involves selecting the materials for the PCB. The most common material is FR-4, a type of fiberglass-reinforced epoxy laminate. The choice of material depends on factors like the PCB's intended application and required electrical properties. 4. Panelization: Multiple PCBs are ofte...